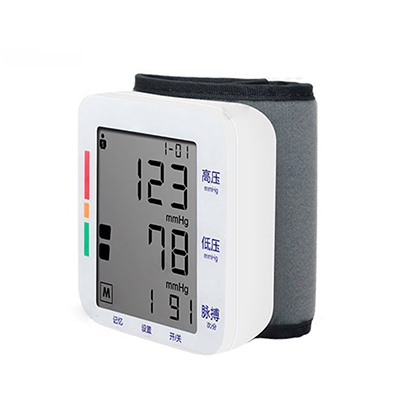
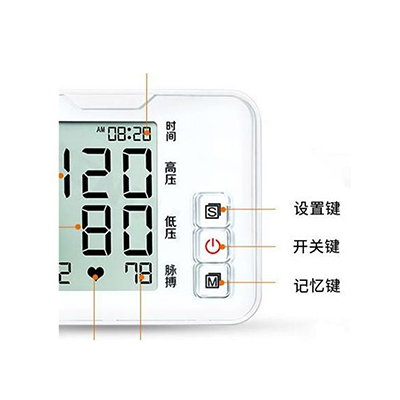
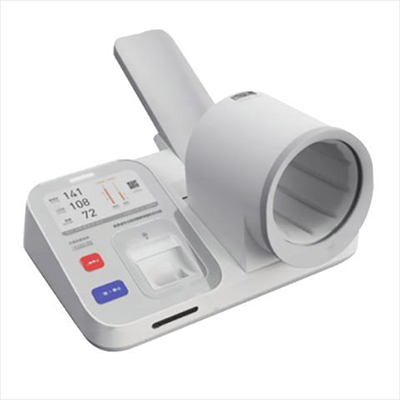
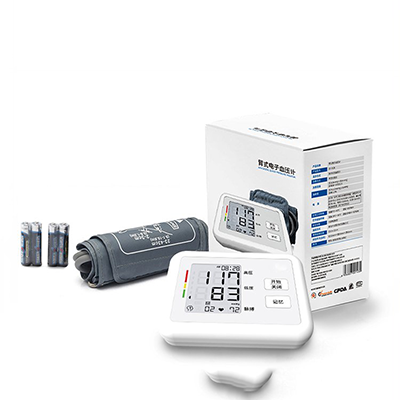
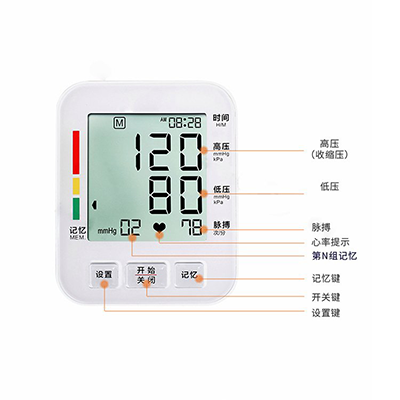
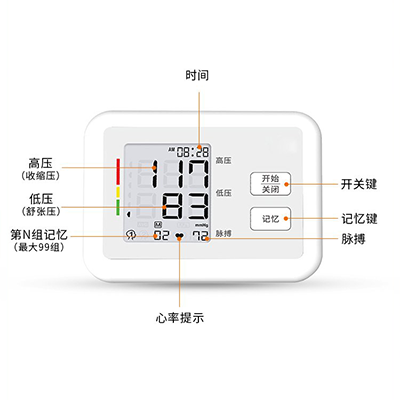
Monitor Veterinary electronic sphygmomanometer
Mercury sphygmomanometer: Based on Pascal's law, the blood flow of the brachial artery is blocked by cuff pressure, and the change of the Korotkoff sound is captured by a stethoscope. When the cuff pressure is higher than the systolic blood pressure, the blood vessel is completely closed. When the pressure drops to the systolic blood pressure level, the blood breaks through the blood vessel wall resistance to form a turbulent flow to produce the first Korotkoff sound, which corresponds to the systolic blood pressure value; when the pressure continues to drop to the diastolic blood level, the blood flow returns to a stable level, and the Korotkoff sound disappears, corresponding to the diastolic blood pressure value
Electronic sphygmomanometer: Using oscilloscope (oscillation method) technology, the pressure fluctuation in the cuff is captured by the pressure sensor. During the pressurization process, the pressure amplitude generated by the vibration of the blood vessel wall is mathematically related to the blood pressure value. The built-in algorithm of the device calculates systolic and diastolic blood pressure by analyzing the peak amplitude and the characteristics of the front and rear fluctuations. Some high-end models also integrate capacitive sensing technology to measure the capacitance value fluctuation caused by the change of blood vessel volume.