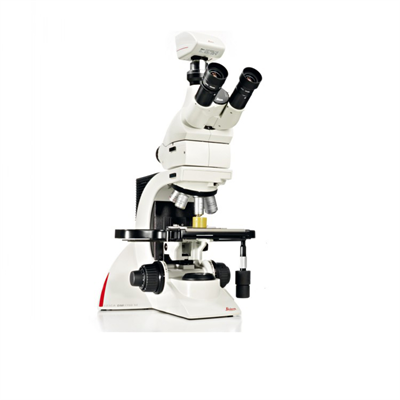
The basic structure of a biological microscope
The basic structure of the biological microscope, the basic structure of the microscope can be divided into three parts: optical system, light source illumination system and mechanical device.
the basic structure of the biological microscope
the basic structure of the microscope can be divided into three parts: optical system, light source illumination system and mechanical device. They are introduced separately below.
First, the optical system of the biological microscope. The optical system of the microscope mainly includes the objective lens, eyepiece, condenser and light source system filters, slides and coverslips.)
(1) Objective lens.
objective lens is generally swirled on the objective lens converter. It is the main component of the microscope. The amplification and resolution of the microscope are mainly played by it. Its advantages and disadvantages determine the main optical properties of the microscope.
(2) Eyepiece
eyepiece is usually inserted on the lens barrel. It can be easily plugged and replaced as needed. Its function is to enlarge the enlarged image of the objective lens further, so that the human eye can clearly observe the specimen. It has two working methods: monocular and binocular. Cheap microscopes are mostly in the form of monocular, and when used, only one eye can be used to observe. Binocular microscopes are equipped with two identical eyepieces, which can be observed by both eyes at the same time. The general eyepiece is composed of two upper and lower lenses or two sets of lenses. A large lens below is called a field lens, and a small lens above is called an eyepiece. There is an annular light bar between the two lenses, which is used to limit the size of the field of view, leaving only images with better imaging quality for observation. It is usually called a field of view light bar. A thin filament is generally glued to the light bar to indicate a specific observation target. When this filament falls, a small section of hair or fine copper wire can be glued instead. But be careful, its tip should fall in the plane of the light bar. Otherwise, when observing, the indication is not clear.
 Microscope skills in detail: from basic to advanced applicat
Microscope skills in detail: from basic to advanced applicat
 A complete analysis of the imaging principles and skills of
A complete analysis of the imaging principles and skills of
 Detailed Explanation of Microscope Imaging Characteristics a
Detailed Explanation of Microscope Imaging Characteristics a
 Here are 20 trivias you didn't know about microscopes!
Here are 20 trivias you didn't know about microscopes!
